TRAIT SELECTION DURING FOOD WEB ASSEMBLY: THE ROLES OF INTERACTIONS AND TEMPERATURE.
Gounand, I., Kefi, S.,Mouquet, N., Gravel, D. (2016).
Theoretical Ecology, doi:10.1007/s12080-016-0299-7
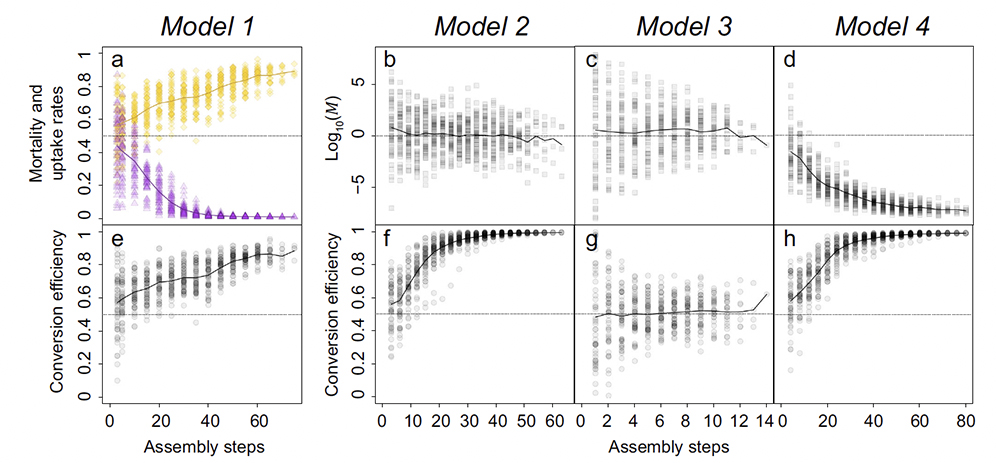
Key message : In this study, we build on classical consumer–resource theory to analyze the implications of the assembly process on trait selection in food webs. Using bioenergetic models, we investigate the selective pressure on body mass and conversion efficiency and its dependence on trophic structure and temperature. We find that the selection exerted by exploitative competition is highly sensitive to how the energy fluxes are modeled. However, the addition of a trophic level consistently selects for smaller body masses of primary producers. An increase in temperature triggers important cascading changes in food webs via a reduction of producer biomass, which is detrimental to herbivore persistence. This affects the structure of trait distributions, which in turn strengthens the exploitative competition and the selective pressure on traits.