THE PARADOX OF ENRICHMENT IN METAECOSYSTEMS.
Gounand, I., Mouquet N., Canard, E., Guichard, F., Hauzy, C. and Gravel, D. (2014).
The American Naturalist, 184, 752-763, doi:10.1086/678406
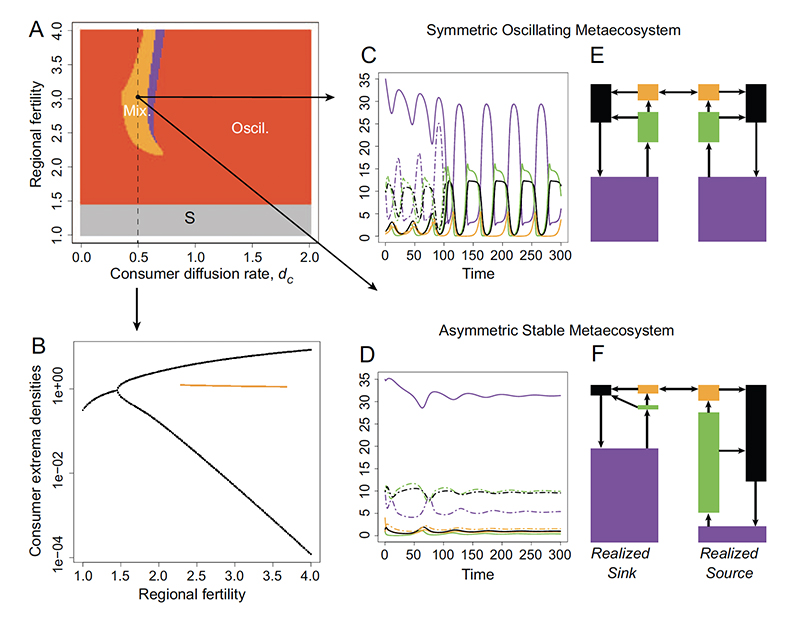
Key message : Here we study the effect of nutrient, detritus, producer, and consumer spatial flows,combined with changes in regional enrichment, on the stability of a metaecosystem model. We considered both spatially homogeneous and heterogeneous enrichment. We found that nutrient and detritus spatial flows are destabilizing, whereas producer or consumer spatial flows are either neutral or stabilizing. We noticed that detritus spatial flows have only a weak impact on stability. Our study reveals that heterogeneity no longer stabilizes well-connected systems when accounting for explicit representation of nutrient dynamics. We also found that intermediate consumer diffusion could lead to multiple equilibria in strongly enriched metaecosystems. Stability can emerge from a top-down control allowing the storage of materials into inorganic form, a mechanism never documented before. In conclusion, local enrichment can be stabilized if spatial flows are strong enough to efficiently redistribute the local excess of enrichment to unfertile ecosystems. However, high regional enrichment can be dampened only by intermediate consumer diffusion rates.